Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor used to treat hypertension, edema, heart failure, and glaucoma. Because carbon dioxide plays a key role in acid-base regulation mechanisms, this class of diuretics is the only one that can affect lung function. Acetazolamide has been shown to interfere with the elimination of carbon dioxide during exercise and also impair muscle drainage, thereby limiting the muscle’s ability to utilize this metabolite and therefore slowing down energy production. This is especially important in the case of long-distance aerobic exercise, although in the aforementioned condition caused by the use of acetazolamide for the athlete, it becomes problematic to manage energy requirements and the elimination of carbon dioxide, thus limiting endurance capabilities. In practice, acetazolamide can cause a decrease in VO2 max during exercise. It should be added, however, that at a high altitude of action, the properties of acetazolamide can reduce disturbances caused by altitude, trivially called mountain sickness, such as headache and nausea, in fact, this substance is used at a dosage of 125/300 mg 1 or 2 times a day, even for climbers when they are about to climb peaks above 4000 m in order to reduce possible disturbances due to hypoxia caused by altitude. Today Viagra is preferred over this drug, which has proven to be more effective.
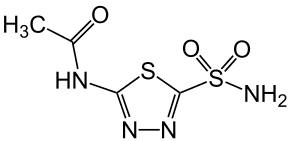
The generalization of the effect of acetazolamide on performance depends on altitude, at low altitudes and under normoxia conditions (normal oxygen concentration in the air, since it is at low altitudes), may impair aerobic performance, instead in hypoxic conditions due to high atmospheres it improves physical abilities.
Furosemide
Furosemide, marketed in Italy as Lasix, is used for the treatment of acute pulmonary edema as well as acute renal failure, therefore in special situations when it is necessary to quickly eliminate fluids.
This substance is given orally or parenterally and lasts approximately 4/6 hours. Furosemide is the main and most active diuretic in the loop, and because of its high potency, it also poses a greater risk of side effects.
Furosemide is the main diuretic used by athletes for weight loss and is masked by other alloying agents, as its effect is the most pronounced of all known substances. It is also regularly used by bodybuilders for a more defined look, although due to the high risk found in its use in recent years, many bodybuilders choose to use potassium-sparing foods or take them together.
Furosemide in high dosages significantly reduces VO2 max in athletes and decreases physical performance for all of the above reasons. Since this substance is especially effective in increasing urine output, it has pretty much all the effects of diuretics.
Some studies on the effects of furosemide have also been conducted in athletes in anaerobic disciplines in which low body weight may have been associated with increased performance, such as jumpers and sprinters (Watson). While weight loss due to high diuresis induced by furosemide has been noted to suggest a possible improvement in these disciplines due to lower weight shift, the results of these studies showed no benefit for athletes practicing it. Kind of activity. Thus, while there is a significant impairment in performance in endurance sports with a high risk of side effects, there is no performance benefit in anaerobic sports using this substance. However, there are few cases of positivity even among sprinters, it is likely that the reaction to the substance is often determined by subjective factors, so laboratory tests do not always reflect the real experience of athletes. It is possible that swimming offers great benefits, as a lighter body swims better, in fact swimmers often test positive for this substance, so frequent use suggests that athletes are finding real improvements in performance, however, they have not done scientific research before orastati. to better assess your swimming performance.
This substance is sometimes also used by dancers and models to appear thinner and lighter , which is especially important in dancing alone in a pair, where the partner has to lift the person.
Furosemide is taken over by bodybuilders on the days leading up to the race, to make them look crisper and drier, using 25 mg every 4/8 hours for the two days leading up to the race, it is most reasonable to use it only on the day of the race to reduce the amount of diamonds. meeting with the use of this substance. It is often associated with other diuretics such as amiloride and potassium supplements for better mineral retention. The aim of this association is to exploit the pronounced effects of furosemide and to reduce the risk of cardiac complications due to potassium loss. Despite these precautions, there are numerous cases of cerebral edema and arrhythmias and heart attacks. In these cases, the most successful athletes are urgently hospitalized and rescued by doctors, but in some cases dramatic events occur, such as a coma and the death of the athlete himself.
Furosemide appears to be particularly effective in masking presence. other substances, in fact, its noticeable effect on urine flow can reduce the concentration of other substances, such as stimulants, by 4/5 times over the next two hours compared to taking them without using furosemide.
