Anabolic agents are chemicals that promote anabolism, that is, the formation of complex molecules, in particular proteins, but not only starting with simpler molecules. These substances are used in therapy to stimulate the growth of certain tissues as needed. They act in a similar way to certain hormones that are responsible for regulating certain growth processes.
There are many classes of these substances, differing in molecular structure and action on the body. Regardless of which class they belong to, they are all molecules that mimic the action of certain hormones or promote their production.
Currently, with the term anabolic substance, we intend to identify those compounds that act to stimulate tissue growth. muscle after increased production of contractile proteins in muscle cells, even though anabolism is a more general term that can also refer to other body tissues. therefore, in this text, the anabolic is considered a substance capable of stimulating muscle synthesis and therefore stimulating the growth of muscle tissue.
Anabolic steroids are anabolic drugs with a molecular structure similar to androgens, capable of mimicking its effects in the body. These drugs are banned by anti-doping regulations, which they represent almost the entire section. These ingredients are also the most frequently monitored substances in tests, as they are used by athletes for extended periods of time to maximize their effects, and because they are found in the body for periods ranging from weeks to many months.
Androgenic hormones
Androgens are defined as a class of hormones responsible for the formation and maintenance of male characteristics. The development of male genital organs and the development of secondary sexual characteristics are treated as such.
Anabolic steroids are synthetic derivatives of natural hormones produced by the body.
Androgenic hormones are a class of substances made from cholesterol from which the body clears a nucleosteroid, a specific molecular conformation common to these hormones and all other hormones called steroids.
The main androgen is testosterone. Beginning in adolescence, testosterone production rises and stabilizes at about 5/7 mg per day for thirty / thirty-five years, after which it begins to gradually decline.
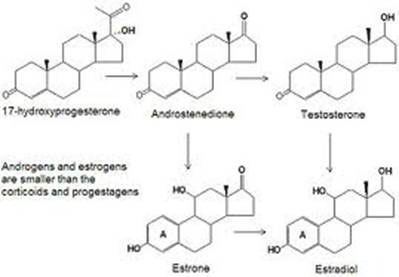
Major Androgens:
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA): Produced by the adrenal glands, it is the main male hormone in women and is also a precursor to estrogen. Several studies show that DHEA increases insulin-like growth factor (IGF-1) and decreases the catabolic effects of cortisol.
Androstenedione: Produced by the testes, adrenal glands and ovaries, it is metabolically converted to intestosterone.
Androstenediol: Produced by DHEA, it is converted by the body to testosterone. produced in supraphysiological amounts by patients with adrenal carcinoma.
Androsterone: produced by the liver through the metabolism of testosterone, has weak androgenic activity.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT): is the more active metabolite of testosterone. It is produced by the enzyme 5α-reductase mainly in the testes and the prostate gland. The greatest activity is given by the greater affinity for the degliandrogen receptor.
Testosterone: is the main male hormone. It is produced in the testes by Lading cells. Estrogen is produced from an aromatase enzyme with an action called aromatization, which produces an aromatic ring, a special molecular constitution. Testosteron propionat regulates sperm production and maturation, libido, penile erection and the development of secondary male characteristics.
